Looking for GPS trackers that last longer without constant maintenance? Here’s what you need to know:
- Battery life depends on usage: Frequent updates (every 30 seconds) drain batteries faster, while daily updates can extend life significantly.
- Choose the right battery type:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion): Rechargeable, lasts 2–3 years, ideal for frequent updates.
- Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂): Non-rechargeable, lasts 5–7 years, perfect for low-maintenance tracking.
- Environmental factors matter: Extreme temperatures and poor signal areas can reduce battery performance.
- Smart features save power: Motion-activated tracking, deep sleep modes, and low-power networks can extend battery life.
For businesses managing vehicles, best GPS trackers for trailers, or equipment, long-lasting GPS batteries reduce downtime and costs. Whether you need frequent updates or long-term tracking, picking the right battery ensures reliable performance.
How Long Does A GPS Car Tracker’s Battery Last? – Talking Tech Trends
sbb-itb-4827db2
Battery Types for GPS Devices
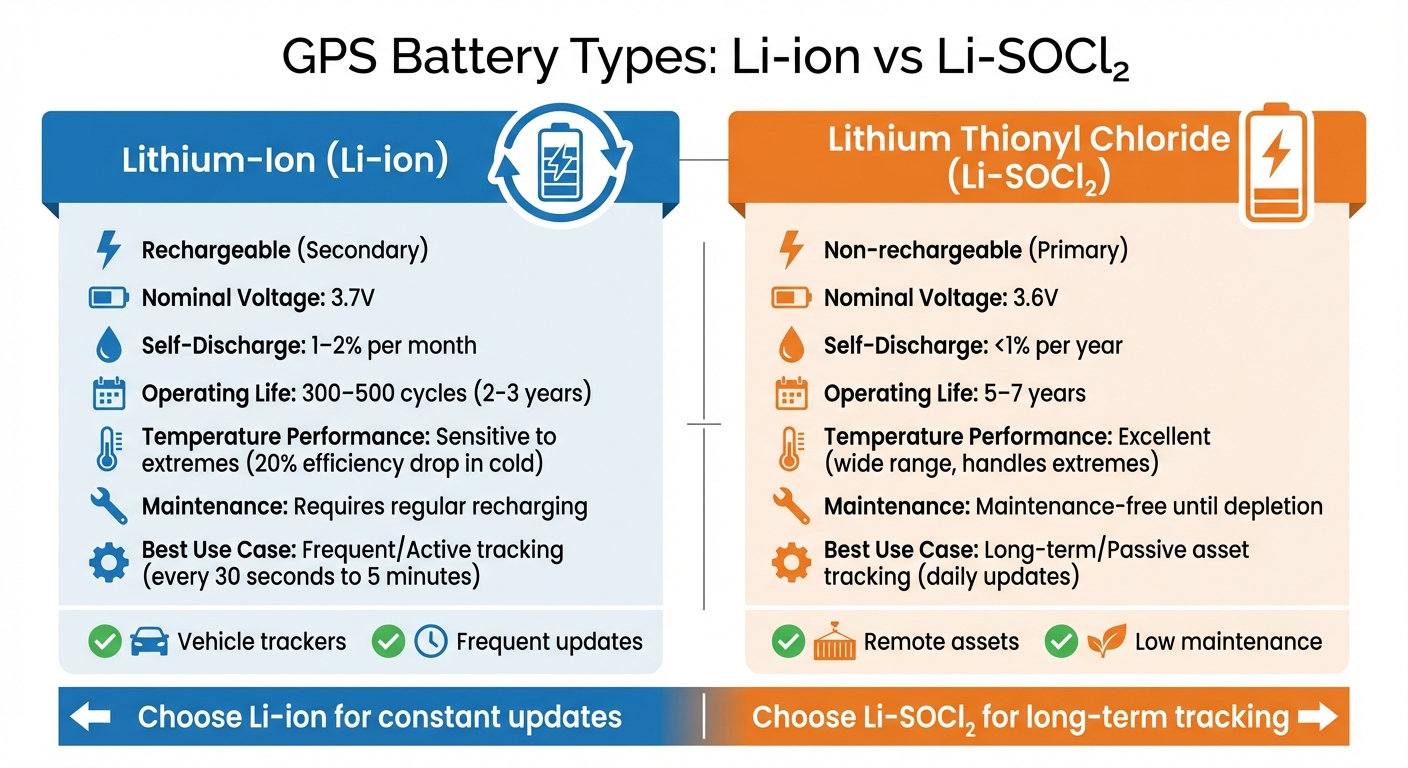
Lithium-Ion vs Lithium Thionyl Chloride GPS Battery Comparison
The type of battery in a GPS tracker plays a big role in how it performs, how often it needs maintenance, and how well it handles tough weather conditions. The battery chemistry affects how often the device can update, how it holds up in extreme environments, and how long it will last overall.
In the world of long-life GPS trackers, two main battery options stand out: lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl₂). If you need frequent updates, go with Li-ion. For long-term, low-maintenance tracking, Li-SOCl₂ is the better choice.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the go-to choice for most rechargeable GPS trackers. They provide a nominal voltage of 3.7V and pack a lot of energy into a small size, making them perfect for vehicle trackers that require updates every few minutes.
These batteries typically last for 300–500 charge cycles, which translates to about 2–3 years of use. They’re rechargeable and lose only 1–2% of their charge per month when idle, ensuring maximum uptime.
However, Li-ion batteries have a downside: they don’t handle extreme temperatures well. In cold weather, their efficiency can drop by up to 20%, and high heat speeds up their wear and tear. They work best in vehicles that have regular access to charging or are hardwired to draw power directly from the vehicle’s battery.
Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂) Batteries
For a low-maintenance option, lithium thionyl chloride batteries are hard to beat. These non-rechargeable batteries provide a nominal voltage of 3.6V and offer the highest energy density available for GPS tracking.
With a self-discharge rate of less than 1% per year, they can remain dormant for years without losing significant power. While standard batteries last weeks or months, Li-SOCl₂ batteries can keep a tracker running for 5–7 years when used for interval reporting (e.g., one update per day).
What’s more, these batteries excel in extreme temperatures. They perform reliably in freezing cold or scorching heat, making them ideal for remote or outdoor assets that don’t have access to frequent maintenance.
Battery Type Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide which battery suits your needs:
| Feature | Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) | Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Rechargeable (Secondary) | Non-rechargeable (Primary) |
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V | 3.6V |
| Self-Discharge | 1–2% per month | <1% per year |
| Operating Life | 300–500 cycles | 5–7 years |
| Best Use Case | Frequent/Active tracking | Long-term/Passive asset tracking |
| Temperature Range | Sensitive to extremes | Excellent (wide range) |
| Maintenance | Requires regular recharging | Maintenance-free until depletion |
To sum it up, pick lithium-ion batteries for trackers that need constant updates – every 30 seconds to 5 minutes. For assets that only need to report their location once or twice a day, lithium thionyl chloride batteries are the better choice.
Next, we’ll dive into the factors that influence GPS tracker battery life.
What Affects GPS Tracker Battery Life
Several key factors influence the battery life of a GPS tracker: how the device consumes power, the surrounding environment, and the technologies used to manage energy efficiently.
Device Power Consumption
How often your GPS tracker updates its location plays a huge role in battery life. For instance, real-time tracking can drain a battery up to 100 times faster than hourly updates. Think of it this way: a 30-second update interval means the device works 120 times per hour, compared to just once for hourly updates. The GPS module and cellular modem are the biggest energy users, especially during a "cold start", when the device connects to satellites for the first time. A "hot start", which uses stored satellite data, is much more efficient.
Modern networks like LTE-M and NB-IoT also help conserve energy compared to older 4G or 2G networks. These newer technologies are designed to use less power, making them a smart choice for extending battery life.
"It’s not just about battery size; it’s about how efficiently that battery’s power is used to keep your vehicle secure."
Environmental Conditions
The environment can seriously affect a GPS tracker’s battery. For example, cold weather can reduce lithium battery capacity by about 20% at 32°F (0°C). On the flip side, extreme heat speeds up chemical degradation inside the battery, shortening its lifespan.
Poor signal areas are another culprit. When the device struggles to maintain a connection, the cellular modem ramps up its transmission power, draining the battery faster. Urban areas with lots of tall buildings – often called "urban canyons" – make the GPS work harder to locate satellites, further increasing power consumption.
Power Management Technologies
Modern GPS trackers are designed to save energy with smarter power management. For instance, motion-activated tracking uses low-power accelerometers to detect movement. The device stays in a low-power sleep mode until motion is detected, at which point it wakes up and starts reporting more frequently.
Deep sleep modes are even more efficient, reducing power consumption to just a few microamperes. Adjusting how often the device reports its location can also make a big difference. Switching from 1-minute updates to 10-minute updates can stretch battery life from a few days to several weeks. Turning off features you don’t need – like LED indicator lights, vibration alerts, or unused Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connections – can also help conserve energy.
"The best long-life GPS trackers in 2026 aren’t just bigger batteries – they’re smarter about power (motion-based reporting, deep sleep modes, low-power networks, and proactive low-battery alerts)."
- Mitch Belsley, Contributor, GPX
Devices like Piritiz Tracking Devices incorporate these advanced power-saving technologies, ensuring reliable performance even in tough conditions.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
To get the most out of your tracker, you need a battery that matches its usage. By aligning battery capacity and chemistry with how your tracker operates, you ensure it performs reliably and efficiently.
Matching Battery Capacity to Your Application
Battery capacity, measured in milliamp-hours (mAh), indicates how much energy a battery can store. The frequency of updates plays a big role in how quickly the battery drains.
For real-time fleet tracking, where updates occur every 1–5 minutes, a rechargeable tracker with at least 10,000 mAh is ideal. With frequent updates, this type of battery can last up to two months. In battery-saver mode, it may last as long as 12 months.
For equipment tracking or trailer security, where assets are usually stationary and only need daily updates, Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂) batteries are a great fit. These high-capacity, non-rechargeable batteries can power unpowered assets like construction equipment for up to five years on a single charge. In these situations, professional-grade tracking solutions often require a battery capacity of 10,000 mAh or more to sustain months of operation.
"A manufacturer’s battery claim is a starting point, not a guarantee. Your actual usage – how often it reports, the signal environment, and how much it moves – will ultimately determine its real-world performance."
- CarLock
Keep in mind that poor reception, like in underground parking or dense urban areas, forces the cellular modem to work harder to maintain a connection. This can drain the battery faster.
Next, consider how the initial cost of the battery compares to its long-term value.
Long-Term Cost vs. Initial Investment
While cheaper batteries might seem appealing upfront, their shorter lifespan can lead to higher costs over time. This is especially true in fleet operations, where frequent replacements add up quickly. On the other hand, non-rechargeable Li-SOCl₂ batteries, though more expensive initially, provide extended operation and reduce the hassle of frequent replacements.
Beyond cost, a battery’s safety and durability features can also impact its long-term value.
Safety and Durability Features
Safety is non-negotiable when it comes to batteries. Look for certifications like IEC62133, which protect against overcharging, short circuits, and fire risks. Additional certifications such as CE, RoHS, and ISO9001 add another layer of assurance.
Batteries with built-in protection circuitry help guard against overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuits. For outdoor or industrial applications, durability is equally important. High-quality GPS batteries are designed to operate in extreme temperatures, from –4°F to 140°F (–20°C to 60°C). Features like IP67 weatherproof ratings protect batteries from dust and water immersion, while rigid casings, such as those found in 18650 cells, offer better resistance to vibration and impact compared to flexible pouches.
For example, Piritiz Tracking Devices include these safety and durability features. Their waterproof designs and long-lasting batteries – up to five years – make them a reliable choice for managing trailers, equipment, and fleet vehicles in tough environments.
Maintaining and Extending GPS Battery Life
Once you’ve picked the right battery, taking care of it properly can make a world of difference. With the right approach, you can add months – or even years – to your GPS tracker’s lifespan.
Proper Storage Practices
When storing spare batteries or taking a tracker offline, temperature and charge level are crucial. Lithium-ion batteries should be stored at 40% to 50% charge, not fully charged or completely drained. Why? A battery kept at 100% charge at 77°F (25°C) loses about 20% of its capacity after a year. But if stored at 40% charge, that loss drops to just 4%.
The sweet spot for storage temperature is 59°F (15°C), though anything between 32°F and 95°F (0°C to 35°C) is acceptable. Aim for 50% humidity, and always remove the battery from the device if you’re storing it long-term to avoid parasitic drain. Also, never let lithium batteries fall below 2V per cell – this can cause permanent damage.
Routine inspections are another must. They help you catch small issues before they snowball into bigger problems.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Keeping your battery in good shape is essential to getting the most out of your GPS tracker. Regular checks can help you spot problems early. While most GPS tracker batteries last 3 to 5 years, you should replace them when their capacity drops below 80% of the original rating. Warning signs like swelling, overheating, or sudden shutdowns are red flags that shouldn’t be ignored.
Also, clean the charging contacts often. Dust and debris can interfere with power transfer. Enable low-battery alerts in your tracking app and set notifications for when the battery hits 15% – this ensures you’re never caught off guard. For rechargeable batteries, keeping the charge between 20% and 80% helps maintain their health over the long term.
Software Updates and Optimization
Don’t underestimate the power of software updates. Firmware updates often include fixes for bugs that drain batteries unnecessarily. After updating, double-check your settings to ensure nothing is causing extra battery drain.
Another major factor is the reporting interval. A tracker that sends updates every 30 seconds uses a lot more power – 120 cycles per hour – compared to one that sends updates hourly. For stationary equipment, you can use motion-activated tracking. This feature keeps the device in a low-power sleep mode (drawing only microamperes) until movement triggers it. You can also save power by disabling secondary satellite systems like GLONASS and sticking with GPS-only.
With tools like the Piritiz Tracking Devices app, adjusting reporting intervals and enabling low-battery notifications is simple. These features help you get the most out of their batteries, which can last up to five years. Learn more at Piritiz Tracking Devices.
Conclusion
Selecting the right battery for your GPS tracker boils down to aligning the battery’s chemistry with your specific needs. For long-term asset tracking, Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li‑SOCl₂) batteries are ideal, offering months or even years of maintenance-free operation. On the other hand, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries work best for devices that are used frequently and can be recharged regularly. However, even the most advanced battery requires effective power management to perform at its best.
Battery life hinges on smart usage. Adjusting reporting intervals and using features like motion-activated tracking can dramatically extend battery performance.
For businesses managing fleets, trailers, or equipment, long-lasting batteries are more than just a convenience – they’re a cost-saving necessity. They reduce downtime for recharging, lower the risk of devices losing power during critical moments, and help control the total cost of ownership. A powerless tracker during a theft is as good as useless, no matter how precise it was beforehand. Piritiz Tracking Devices, for example, offer up to five years of battery life, feature a waterproof and wireless design, and come with a mobile app for easy monitoring. You can explore more at Piritiz Tracking Devices.
With the right battery choice, optimized settings, and consistent maintenance, your tracking system becomes a dependable tool. As highlighted earlier, proper care further enhances battery longevity, ensuring your assets stay monitored when it matters most.
FAQs
How do environmental factors influence GPS battery life?
The environment can have a big impact on how long your GPS device’s battery lasts. Extreme temperatures – whether it’s freezing cold or scorching hot – can take a toll on battery performance. In cold weather, the chemical reactions inside the battery slow down, which causes it to drain faster. On the flip side, excessive heat can wear down the battery over time, reducing both its capacity and overall lifespan.
Humidity and moisture are also factors to watch out for. If your device isn’t waterproof or properly sealed, exposure to high humidity or water can lead to corrosion or internal damage, which can significantly shorten the battery’s life.
To keep your GPS device running smoothly and reliably, it’s essential to think about these environmental factors, especially if you’re using it outdoors or for extended periods.
What’s the difference between Li-ion and Li-SOCl₂ batteries for GPS devices?
Li-ion batteries are rechargeable, lightweight, and pack a lot of energy into a compact size. This makes them a solid choice for GPS devices that are used often and need frequent recharging. They’re commonly found in gadgets where portability and regular charging are essential.
Li-SOCl₂ batteries, however, are non-rechargeable but deliver even higher energy density. They also perform exceptionally well in extreme temperatures. These batteries are perfect for long-term applications, like GPS trackers designed to run for years without needing a battery change.
What are the best ways to extend the battery life of my GPS tracker?
To get the most out of your GPS tracker’s battery, start by using power-saving modes or standby features if they’re available. These settings help conserve energy by scaling back non-essential functions while keeping the core tracking operational.
You can also save battery by tweaking the signal update frequency. For instance, setting location updates to every 15 minutes instead of every minute can go a long way in preserving power.
Don’t overlook regular upkeep, either. Keep the device clean and free from dirt, and ensure it’s used in proper conditions. Opting for a tracker with a high-capacity battery – like lithium-ion or lithium-polymer – can also boost its longevity.
Using these tips, you’ll cut down on the need for frequent recharges or replacements, keeping your tracker running longer when you need it most.






