Protecting GPS data is more critical than ever. With increasing threats like GPS spoofing, jamming, and AI-driven cyberattacks, businesses relying on tracking devices must prioritize security. Key steps include using strong encryption (AES-256, ECC), implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), and deploying AI-powered threat detection. Access control measures like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and regular audits further reduce risks. Cloud-based platforms simplify data management while enhancing security, and employee training helps combat phishing and social engineering attacks. Follow these strategies to safeguard your GPS systems and maintain operational reliability. Learn how tracking devices protect equipment and fleets from theft.
Use Strong Encryption Protocols
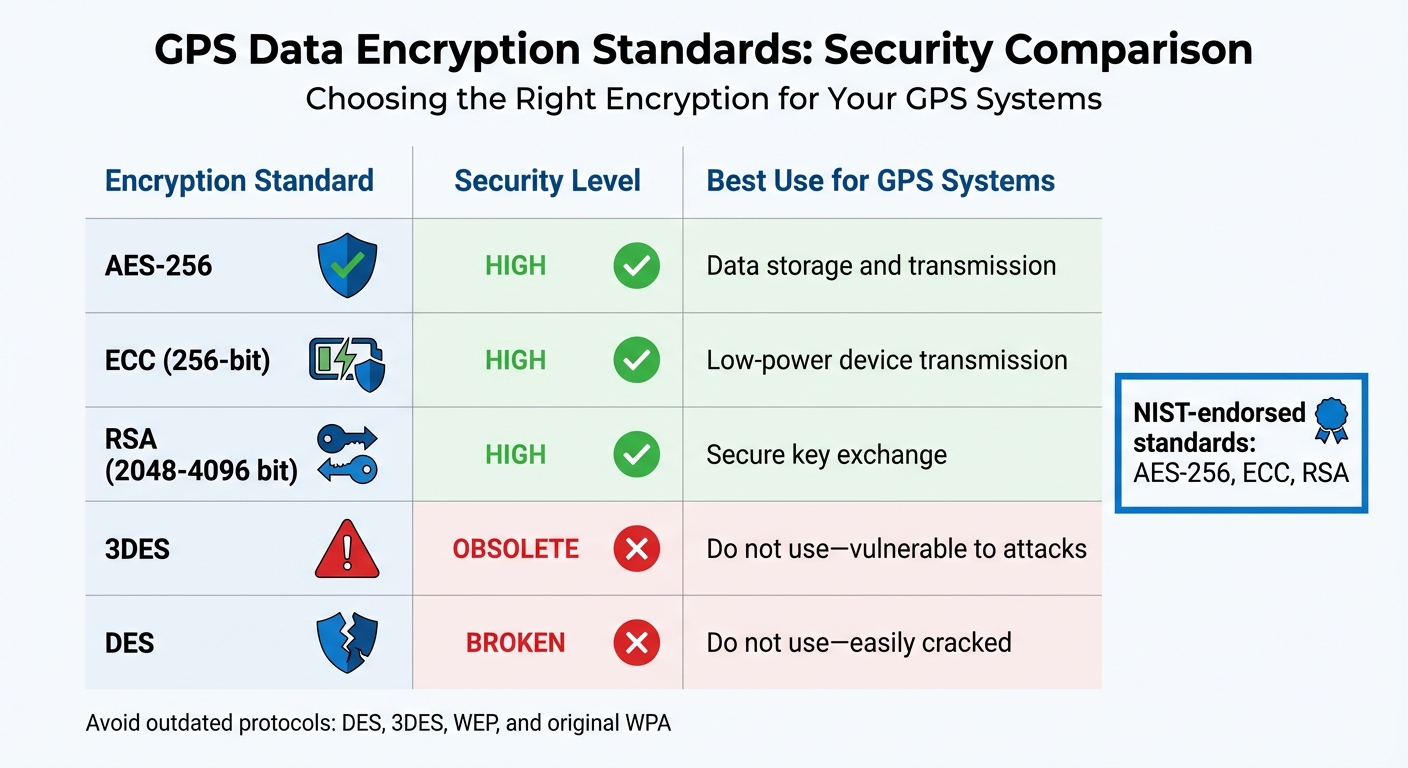
GPS Data Encryption Standards Comparison 2025
Encryption is the process of converting GPS data into unreadable code, ensuring that only authorized users can decode it. This protects sensitive information during both transmission and storage. However, the key challenge lies in selecting encryption methods that can withstand both current and future cyber threats.
Recommended Encryption Standards
AES-256 is widely regarded as the gold standard for GPS data protection. It employs 256-bit keys to defend against brute-force attacks and is endorsed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). AES-256 is critical for securing data both at rest (stored on devices or servers) and in transit (transferred between devices or platforms).
Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) is another powerful option, offering strong security with 256-bit keys. Its efficiency makes it ideal for low-power devices. Meanwhile, RSA encryption – with key sizes ranging from 2,048 to 4,096 bits – is essential for establishing secure key exchanges when devices connect to GPS tracking platforms.
For comprehensive protection, combine full-disk encryption with secure transmission methods like VPN or TLS. This ensures data remains protected during storage and transfer.
Chad Kime, Lead Writer at eSecurity Planet, highlights the importance of staying ahead with encryption technologies:
"The strongest encryption of the 1970s didn’t survive replacement by stronger encryption in the 1990s. Yet those once-strongest encryption options of the 90s now show weaknesses to modern computing power".
Avoid outdated protocols such as DES, 3DES, WEP, and the original WPA, as they are highly vulnerable to modern attacks. Cryptographic failures are ranked as the second most critical vulnerability in the OWASP Top 10, primarily due to the continued use of weak encryption methods.
| Encryption Standard | Security Level | Best Use for GPS Systems |
|---|---|---|
| AES-256 | High | Data storage and transmission |
| ECC (256-bit) | High | Low-power device transmission |
| RSA (2048-4096 bit) | High | Secure key exchange |
| 3DES | Obsolete | Do not use – vulnerable to attacks |
| DES | Broken | Do not use – easily cracked |
To maintain strong security, it’s essential to not only select robust encryption methods but also update them regularly.
Keep Security Protocols Updated
Even the best encryption methods lose their effectiveness over time as computing power increases and attack techniques evolve. For instance, computing power roughly doubles every two years, which means encryption standards must be continuously reviewed. While AES-256 remains strong today, NIST warns that quantum computing could threaten its integrity within the next two decades.
More immediate concerns come from AI-driven attacks. Cybersecurity strategist Matthew Rosenquist explains how automated exploit tools operate faster than traditional defenses can keep up:
"Quarterly or even monthly patching cycles become woefully insufficient".
Organizations must routinely assess their encryption protocols and proactively retire outdated methods before they become vulnerabilities. Effective key management is also critical, as attackers often target encryption keys to bypass algorithms entirely. Protecting these keys ensures that GPS tracking data remains secure throughout its lifecycle.
Practical steps include using the longest key length your hardware supports (e.g., 256-bit instead of 128-bit), regularly updating encryption protocols, implementing centralized key management systems to automatically rotate keys, and conducting frequent security audits to identify and address any use of outdated encryption methods. If your GPS devices store tracking logs internally – some can hold up to two weeks of encrypted data – ensure that this stored information is secured with the latest encryption standards.
Looking ahead, the development of quantum-resistant algorithms is already underway for high-security applications. While these methods aren’t yet mainstream for commercial GPS tracking, staying informed will help you prepare for future upgrades before they become urgent.
Strengthen Access Control and Authentication
While encryption protects data during transmission, controlling access is essential to defend against both external and internal threats. Encryption locks the data, but access control determines who holds the keys. To secure GPS data effectively, a combination of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and regular audits provides a strong defense.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC ensures users can only access the GPS data they need for their specific roles. For example, drivers might only see their assigned routes, while fleet managers oversee the entire system using GPS trackers for trailers. This approach embraces the principle of least privilege, reducing unnecessary exposure to sensitive location data.
RBAC is a cornerstone for 60% of organizations managing identity and access. By limiting permissions, RBAC minimizes the damage an attacker could cause if a single account is compromised. IBM explains it well: "RBAC mitigates the damage that a hacker can do with a user’s account by limiting what that account can access in the first place".
Insider threats also pose a serious risk. Data breaches involving malicious insiders cost an average of $4.92 million, well above the overall average breach cost of $4.44 million. Restricting permissions can make it significantly harder for employees to misuse GPS data, whether intentionally or through negligence.
To implement RBAC effectively:
- Start by cleaning up outdated permissions and removing unnecessary access.
- Use opaque device IDs like UUIDs instead of personal identifiers like email addresses or phone numbers when managing GPS tracking devices for equipment.
- Regularly review roles and permissions to prevent "permission creep", where users accumulate access they no longer need.
Here’s a quick breakdown of RBAC models and their applications:
| RBAC Model | Key Feature | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Core (Flat) RBAC | Basic role-to-permission mapping. | Small organizations or foundational security. |
| Hierarchical RBAC | Roles inherit permissions from lower levels. | Companies with clear reporting structures. |
| Constrained RBAC | Enforces Separation of Duties (SOD). | High-security tasks requiring dual approvals. |
| Symmetric RBAC | Includes periodic permission reviews. | Large enterprises focusing on least privilege. |
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Building on RBAC, MFA adds another layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication. Even if one set of credentials is stolen, MFA ensures that unauthorized access is much harder to achieve.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) categorizes MFA strength using Authentication Assurance Levels (AALs). Higher levels, such as AAL2 and AAL3, demand phishing-resistant methods and significantly increase the difficulty for attackers. For maximum security (AAL3), use public-key cryptography with non-exportable authentication keys.
To strengthen your MFA strategy:
- Implement per-session MFA for critical resources. For instance, Teleport‘s system issues an MFA challenge whenever a user requests a one-time certificate to access a resource, blocking attackers from exploiting compromised sessions.
- Enable dual authorization for sensitive changes, requiring approval from multiple reviewers to prevent privilege escalation from a single compromised account.
- Use "step-up" authentication protocols to increase security levels when users attempt to access more sensitive GPS data or perform administrative tasks.
Perform Regular Access Audits
Regular audits are essential to ensure permissions remain up to date and appropriate for users’ current roles. These audits can also detect account abuse, such as unauthorized access or unusual activity patterns that might indicate GPS jamming or spoofing attempts.
Auditing best practices include:
- Assigning a "role owner" within each department to verify that permissions align with current needs.
- Reviewing session logs for timestamps, actions, and device details to identify anomalies. This data is especially critical for industries like healthcare and finance, which require transparency for compliance.
- Combining audits with Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA) models, where permissions are continuously verified rather than granted indefinitely.
As Fortinet notes, in Symmetric RBAC models, roles are more dynamic and require regular review to prevent unused permissions from accumulating. By staying proactive with audits and leveraging tools like ZTNA, you can ensure your GPS tracking system remains secure, even as your organization grows and evolves.
Set Up Threat Detection and Real-Time Alerts
Once access controls are in place, the next step is deploying systems that actively detect threats as they happen. This approach goes beyond the reactive methods of traditional security, which often wait until after a breach to respond. Modern GPS tracking systems require a more vigilant strategy – one that identifies unusual activity before it turns into a full-blown security issue.
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection
Artificial intelligence shines when it comes to spotting patterns that might go unnoticed by human eyes. By analyzing normal GPS activity – such as typical routes, login times, and data access behaviors – AI systems establish a baseline. When something deviates from that baseline, the system immediately flags it. For instance, if a driver accesses location data for vehicles outside their assigned fleet or if login attempts suddenly spike from an unexpected geographic area, the system sends an alert.
Organizations leveraging AI-driven governance have reported a 60% drop in data leakage risks. In one case from July 2025, a financial services company handling sensitive customer data used AI enforcement to shrink their breach exposure window from weeks to just minutes while nearly eliminating false positives. These systems don’t just detect threats – they enforce policies in real time, stopping inappropriate access before it even happens.
"AI-Driven Governance will become the standard, with intelligent systems automating increasingly complex security decisions based on organizational policies and learned patterns." – Velotix
Switching from static Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) is another key step. Unlike RBAC, which assigns fixed permissions, PBAC dynamically evaluates access requests based on factors like time of day, device type, location, and user behavior. This ensures permissions adjust automatically to fit the context. To make the most of this system, centralize activity logs across all servers, firewalls, and cloud services. This gives AI tools full visibility, enabling them to detect patterns and configure alerts for high-risk events like repeated failed logins, privilege escalation attempts, or unusual data transfers. This dynamic setup also supports advanced measures like geofencing for continuous monitoring.
Geofencing for Boundary Monitoring
Geofencing uses GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, or cellular data to create virtual boundaries around specific locations. When a tracked vehicle or asset crosses one of these boundaries, the system instantly notifies managers. This makes geofencing a powerful tool for theft prevention. For example, if a high-value trailer leaves your facility after hours, you’ll know right away.
Geofencing isn’t just about security – it’s also useful for managing operations. Fleet managers can set zones around customer sites, warehouses, or restricted areas. If a driver strays off their assigned route or enters an unauthorized zone, the system sends real-time alerts through mobile apps or web platforms. Additionally, GPS trackers with motion sensors can detect tampering or unauthorized movement, adding an extra layer of protection. For even greater security, consider embedded GPS devices that connect directly to a vehicle’s power supply and stay hidden from potential thieves.
Protect Against GPS Jamming and Spoofing
To complement anomaly detection and geofencing, it’s critical to guard against interference threats like GPS jamming and spoofing. Jamming blocks GPS signals entirely, while spoofing feeds false location data to your system. To counter these tactics, many trackers now use hybrid connectivity, combining satellite and cellular networks to maintain communication even if one signal source is disrupted.
Monitoring current movements against historical routes can also help detect tampering. If a vehicle suddenly appears far off its usual path or if location data shows impossible speed changes, these are clear red flags that require immediate attention. Long-term undetected intrusions are especially concerning. As Carolyn Friedman, Illinois Assistant Attorney General, explains:
"If they not only managed to intrude, but then they remain and they’re undetected for a long period of time. That’s a signal that there’s more conflict."
To ensure devices remain secure, perform regular maintenance checks. This includes evaluating device security, battery performance, and software updates to keep threat detection features functioning properly.
sbb-itb-4827db2
Choose Cloud-Based Platforms for Data Management
Benefits of Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Cloud platforms are a game-changer for GPS data management, offering centralized tools and automated defenses that boost security and simplify operations. With features like automatic encryption – both at rest and in transit – these platforms ensure data remains protected. For added control, many services provide customer-managed symmetric keys, allowing you to handle key rotation and deletion directly. This layered security approach means that even if one safeguard falters, your tracking data stays secure.
Integration with centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems ensures that access is limited to only those who need it, sticking to the principle of least privilege. Additionally, cloud services often automate data lifecycle management. For instance, Amazon Location Service automatically deletes device position history after 30 days, minimizing long-term exposure and eliminating the need for manual deletions.
Monitoring tools like AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch provide real-time insights, helping detect unusual activity such as unauthorized access attempts or suspicious data transfers. On top of that, many cloud providers anonymize and encrypt data before it’s transmitted, preventing unauthorized use or data sales.
What to Look for in Cloud Solutions
When choosing a cloud-based GPS platform, security should be your top priority. Ensure the system uses HTTPS for data transmission to safeguard against interception. Look for platforms offering position filtering options – such as distance-based, time-based, or accuracy-based filters – to minimize unnecessary data storage while improving privacy. These filters help eliminate insignificant movements or signal inaccuracies, storing only meaningful location updates.
Durable hardware is equally important. Opt for devices with waterproof and shockproof (IP-rated) designs to maintain consistent signal quality, even in harsh conditions. Tamper alerts are another must-have; you’ll want instant notifications if a device is disconnected or loses power. To further protect personal information, choose systems that use opaque device identifiers like UUIDs.
A strong platform should also include a user-friendly mobile app with secure APIs that integrate seamlessly with your existing business tools. Real-time refresh rates are critical for immediate responses to theft or unauthorized movements – trackers that update every few seconds are ideal, while slower refresh rates may cause delays. Lastly, check how long the platform retains historical data. While 30 days is standard, some solutions extend this to 12 months for added flexibility.
These features collectively ensure a secure, efficient, and user-friendly GPS tracking experience, as demonstrated by Piritiz.
Piritiz: A Secure GPS Tracking Solution
Piritiz offers GPS tracking devices tailored for vehicles, trailers, and equipment, combining security with ease of use. Designed for rugged outdoor conditions, these devices are battery-powered (lasting up to five years), waterproof, wireless, and simple to install.
The Piritiz platform includes a mobile app that provides 24/7 access to live map views and instant alerts for movement or tampering. This real-time tracking not only deters theft but also enables quick recovery of assets if they go missing. For fleet management, Piritiz includes reporting tools to help optimize routes and monitor vehicle usage patterns. Flexible monthly plans start at $9.95, with discounts for longer commitments, making this a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
Train Employees on Data Security
Even with advanced technical safeguards, a single misstep – like an employee clicking on a malicious link or mishandling sensitive GPS data – can jeopardize your entire operation. As CISA puts it, "Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility and we each have a part to play". This underscores the importance of training everyone in your organization, from drivers to top executives, on protecting tracking data.
Make training straightforward and actionable. Encourage employees to adopt a "Stop before you post, share, or send" habit, which means pausing to verify the source before responding to any request for GPS data or system access. This simple practice can block many social engineering attacks. Below are strategies to help reduce risks tied to human error and social engineering.
How to Prevent Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering are major threats to data security, especially with AI-powered tactics like deepfakes that can bypass traditional defenses. One effective way to prepare employees is through scenario-based exercises. For instance, simulate urgent requests for vehicle locations to help staff recognize warning signs. These realistic exercises can sharpen their ability to detect threats before they encounter them in real-world situations.
Instead of relying solely on annual training sessions, consider micro-learning techniques. The Center for Development of Security Excellence suggests using "Cybersecurity Shorts" – quick, easy-to-digest updates that keep security top of mind. Reinforce these lessons with visual reminders, like posters in break rooms and digital workspaces. Additionally, take advantage of CISA’s free cybersecurity awareness toolkits. These resources cover topics ranging from spotting suspicious emails to understanding how attackers manipulate Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) signals through jamming or spoofing.
Guidelines for Handling GPS Data Safely
Technical safeguards are crucial, but clear operational guidelines are just as important for maintaining data integrity. Start by defining strict rules for accessing and sharing GPS data. Use secure collaboration tools instead of standard email for sharing sensitive information. For example, the Homeland Security Information Network – Critical Infrastructure (HSIN-CI) offers free tools for real-time collaboration, document sharing, and instant messaging to eligible private sector operators.
Another key step is implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework tailored for PNT services. The NIST IR 8323 Rev. 1 provides a structured approach to managing risks associated with systems and networks that rely on PNT services. GPS signals are vulnerable to disruptions – whether natural, accidental, or intentional – and employees should be trained to spot signs of interference. For example, if a GPS device displays erratic behavior or unexpected location changes, staff should know how to report these incidents immediately. Executive Order 13905 highlights the importance of responsible PNT use, emphasizing that the nation’s security depends on the reliable functioning of critical infrastructure.
Keep training programs ongoing to address the constantly evolving threat landscape. Use events like Cybersecurity Awareness Month to reinforce key practices and remind employees that "when we all take simple steps to be safer online – at home, in the workplace, and in our communities – it makes using the Internet a more secure experience for everyone".
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Summary of Best Practices
Protecting GPS data in 2025 requires a combination of technical safeguards and operational strategies. Encryption protocols act as the cornerstone of your security, while role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensure that sensitive location data is only accessible to authorized individuals. Incorporating real-time threat detection through AI-driven anomaly monitoring and geofencing helps identify suspicious activities as they occur. Centralizing data management on cloud-based platforms not only simplifies operations but also strengthens security measures. Lastly, ongoing employee training addresses the human element, which remains a critical vulnerability in any security system.
These measures provide a clear framework for securing GPS data effectively.
How to Get Started
To begin, conduct an audit of your critical assets and identify which ones require tracking and protection. With more than 80% of small businesses still relying on manual methods, transitioning to a cloud-based platform is a logical first step to secure data and improve efficiency. Start with your most critical assets, then gradually expand your coverage as you become more comfortable with the system.
For immediate security improvements, focus on the essentials: enforce strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, schedule regular software updates, and set up geofencing alerts. The cost is manageable, with real-time tracking services starting at around $10 per month, making advanced security solutions accessible even for smaller businesses. If you encounter any cyber threats, report them right away to CISA at 1-844-Say-CISA to contribute to a safer infrastructure for everyone.
FAQs
How does AI improve GPS data security against modern threats?
AI is transforming GPS data security by stepping in to detect and address potential threats as they happen. Using advanced machine learning, AI can monitor typical device behavior – like movement patterns and signal strength – to spot unusual activity, such as spoofing, jamming, or unauthorized access. It also streamlines processes like rotating encryption keys and validating data, ensuring every location update remains secure and easy to trace.
But detection is just the start. AI also enables swift, automated responses. When a threat is identified, it can isolate compromised devices, shift them into a secure low-power mode, and alert operators right away. This kind of proactive defense shields GPS systems from emerging threats, including those powered by AI-driven hacking, making GPS tracking more secure and dependable as we move into 2025 and beyond.
What are the advantages of using cloud-based platforms to manage GPS tracking data?
Cloud-based platforms offer a reliable and secure way to manage GPS tracking data. By encrypting all data transfers, they safeguard sensitive information as it moves between devices and the cloud. Plus, administrators can set precise access controls, ensuring team members only have the permissions they need. This not only simplifies managing security but also minimizes potential risks.
These platforms take care of storage and processing automatically, guaranteeing seamless access to real-time tracking information – even during peak usage. Built-in monitoring and logging tools make it easy to track activity, spot irregularities, and stay compliant without additional hassle. For Piritiz users, this means round-the-clock secure access to vehicle, trailer, and equipment locations via a user-friendly mobile app. Meanwhile, the platform handles encryption, scaling, and system management quietly in the background.
Why is employee training important for protecting GPS tracking data?
Employee training plays a key role in protecting GPS tracking data by helping staff recognize the risks tied to exposing sensitive location details – like routes, schedules, or asset positions. This knowledge minimizes the likelihood of theft, unauthorized access, or disruptions to operations. By educating teams on encryption, strong authentication methods, and safe data-handling practices, businesses can strengthen their overall security measures.
Training also encourages accountability, equipping employees to spot phishing attempts, report suspicious device activity, and properly use security tools such as geo-fencing. An informed workforce ensures GPS tracking systems, like those from Piritiz, are used safely, safeguarding critical data while optimizing the advantages of real-time tracking and improved efficiency.






